Last fall, I completed the third edition of my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected: A Teachers’ Guide to the Tree of Life. This came only six years after the second edition, which in turn came eight years after the first edition. “Why all this change?” you may ask.

I found that updates were needed because of changes in biologists’ view of the diversity of life. The data about how organisms are related continue to pour in, and because of this, the details of lineages and relationships change. You may be tempted to wait until the field stabilizes and stick with older ideas. Children, however, need a useful view of the diversity of life, even if it will be somewhat amended later. They cannot build on a foundation that is clearly obsolete. Specifically, it is no longer useful to present children with Five or Six Kingdoms, and those charts need to go in your history-of-science file.
I updated Kingdoms of Life Connected from cover to cover. I redid the lists of learning resources – books and websites; I purged links that no longer worked and added new ones. Publishers and authors have brought forth valuable new books in recent years, and I added titles to the lists while retaining older but useful books. I revised all the text, including the activities and lesson suggestions. I fact-checked the information to make sure it was as up to date as I could make it.
There is one especially important addition, a new lesson for introducing to the Tree of Life chart to beginning elementary children. This lesson gives older children important concepts as well, particularly if they have not yet had this overview. The introductory lesson leads children to the idea that all life shared a common ancestor and is connected. It shows them the relationships between the major branches of life. For example, they learn that the animals and fungi are sister lineages and that plants are only distantly related to fungi.
I’ll give a brief summary of some of the changes below. For more information, see the book, which is available at https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/kingdoms-of-life-connected-third-edition (printed version). The ebook (pdf) is at https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/kingdoms-of-life-connected-third-edition-ebook.
There are no big changes in the prokaryotes. I have kept a very basic approach because it takes extensive knowledge of biochemistry to understand the many branches of bacteria and archaea. Introductory college biology texts present a few basic lineages, and I felt that this approach would be good for children as well.
In the protists, I rearranged the Excavata lineage on the Tree of Life chart. Now, the euglenazoa and kinetoplastids are sister lineages and the metamonads are the first branch. I expect that Excavata will be split apart and redone in the future. It probably won’t be a eukaryotic supergroup, but studies continue to confirm the other supergroups – Archaeplastida, SAR, and Amorphea.
Scientific terminology evolves, and I was happy to see a complicated name go away. The branch of the stramenopiles and alveolates was previously called Chromalveolata, but that term has fallen out of favor. It originally described a lineage that included two branches I didn’t show, the cryptophytes and haptophytes; these are now placed elsewhere on the Tree of Life. The branch of the stramenopiles and alveolates may get a new name, but it seems best to leave that branch blank for now.
The fungi were the major branch that changed the most. The former Zygomycota lineage is now divided into two main lineages, the Mucoromycota and the Zoopagomycota. On my Tree of Life chart, I show the larger one, Murcoromycota. Its branches include the pin molds or Mucoromycotina (black bread mold, for example) and the arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi or Glomeromycotina (AM fungi). The AM fungi were previously placed on their own branch, but they have been added back to Mucoromycota. I didn’t add the Zoopagomycota to the Tree of Life chart, but if you have children who are interested in learning more, Fungarium by Katie Scott and Ester Gaya, is a good book for launching their explorations.
In the animal kingdom, studies have clarified some relationships in the protostome branch. You can give children the term “Spiralia” for the lineage previously called Lophotrochozoa. The whole branch is called Spiralia; “Lophotrochozoa” still refers to the mollusks and annelids. It is another of the situations where it is useful to know an older and newer term. “Lophotrochozoa” has been used for the Spiralia branch for about 20 years, and it appears in a number of websites. I recommend looking to the future and using “Spiralia” primarily. It is certainly easier to say and spell.
In the plant kingdom, studies have resolved several questions about the bryophytes. They are a single branch of life, a monophyletic lineage. The first branch was recently determined to be the hornworts. The mosses and liverworts are sister lineages. The older story was that the liverworts were the first branch because they do not have stomata. It appears that their ancestors lost their stomata rather than never having them.
The virus chapter now has suggestions for making a model of a coronavirus. I published this chapter as a stand-alone pdf in 2020. Note that if you have the third edition of Kingdoms of Life Connected, you already have the content of “What Is a Virus?”.
It is easy to become overwhelmed by all the names and branches of life. I recommend that you concentrate on the larger branches on the Tree of Life and continue to other branches as children (and you) learn about these and are interested in pursuing more. For in-depth studies at the elementary level, I recommend the digging further into the animal and plant kingdoms.
Start with the big overview of the Tree of Life. After that, my learning material, Sorting Branches on the Tree of Life: Vertebrates and Plants, is a good place to go. It is available as a pdf that you can print https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/sorting-branches-on-the-tree-of-life-vertebrates-and-plants or as a printed material https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/copy-of-sorting-branches-on-the-tree-of-life-vertebrates-and-plants-file-for-printing.

Enjoy your explorations of the Tree of Life!
It’s that time of year when the urge to put things in order can strike. You may have a closet with a lot of biology materials that you want to evaluate. Here are my suggestions for things to throw out. You may not want to discard the whole material just because it has flawed content provided it is feasible to fix the problems.
In the animal kingdom materials, if you find anything that has the phylum Coelenterata, please remove that name or cover it. Biologists haven’t used it for more than 30 years. That phylum was split into two others when biologists discovered that it held two unrelated groups. The two lineages are called phylum Cnidaria (anemones, corals, and jellyfish) and phylum Ctenophora (comb jellies). It is likely that you can cover over “Coelenterata” and add the label “Cnidaria.” Just make sure that you don’t have comb jellies in with your cnidarians.
Another no-no for the animal kingdom is showing protozoa along with the animals. This goes back to the two-kingdom idea of classification, and biologists and biology textbooks haven’t grouped protozoans with animals in more than 40 years.
If you find a chart that is labeled “Non-Chordates,” change the title to “Invertebrates.” Maybe “non-Chordate” was useful in the past, but biologists use “invertebrate” far more often. I searched books on Amazon.com using “non-chordates,” and I got six titles, all published outside the US. I searched “invertebrates,” and got over 6000 titles. A non-chordate chart isn’t likely to show current information, so it is time to recycle it or at least recycle the images and add new text.
The relationships between the phyla of animals solidified about 15 years ago. In biology, classification has morphed into systematics, which all about relationships and shared common ancestry. The details of this would take several blogs so I will simply say that the arthropods are related to the nematodes, and the mollusks are related to the annelids. Arthropods were once grouped with annelids, but that is no longer considered valid. Can you add something to your animal kingdom chart that shows which phyla are closely related? See my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected, for help if your animal kingdom chart needs a redo. https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/frontpage/products/kingdoms-of-life-connected-second-edition. It is also available as an ebook (pdf).
Dig back into the cobwebs in the botany section of your closet. If your chart of the plant has club mosses separated from the fern clade – whisk ferns, horsetails, and ferns – you have a good representation of life’s diversity. The chart from InPrint for Children is a good example. https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/montessori-botany-materials/products/plant-kingdom-chart . Another mark of a current material – it should use the term “eudicots” instead of “dicots.” If your chart has phylum names, it is quite possible that many of the names are obsolete. Many botanists no longer use phyla or division names. Instead, they use lineage names, and sometimes a common name is all you need. I have a graduate level botany textbook that uses no phylum/division names.

If your plant kingdom chart has fungi or bacteria on it, the time has come to do some serious pruning. Those two have to go to their own charts. If the image of a fungus appears on a plant kingdom chart, that’s what children will remember even if you say that it doesn’t belong there. The fungus kingdom is a sister to the animal kingdom. In nature, fungi and plants are partners, but on classification charts, they shouldn’t hang around together.
If you have a Five Kingdoms chart, file it under the history of biology. It should NOT be the first thing children see as they study the diversity of life. The Tree of Life is the place to start.
How about your timeline of life? This is a difficult material to do well, and there are many bad attempts out there. Does your timeline show several red lines coming together (converging)? That’s the traditional style, but lineages do not converge (fuse together); they diverge (split apart). Maybe you could salvage the images and redo the timeline without the misleading lines. Check the dates for the fossils because there are several in the wrong place on the older timelines.
Does your timeline of life have photos of extant animals or plants in prehistoric times? This gives a very wrong impression. I’ve seen a timeline that had “First marsupial” and a picture of a kangaroo. This is just like saying “First eutherian (placental) mammal” and showing a picture of a horse. Both the kangaroo and the horse evolved within the last few million years. They are both adapted to live on grasslands and open shrub lands, where resources are spread out, and there is little cover from predators. Therefore both are good at moving quickly over long distances. Neither one of them belongs in the Mesozoic Era on a timeline of life. Mesozoic mammals were much smaller and less specialized.
Does your timeline have the five major extinctions? And does it have ice ages in the right places? The older charts used ice to symbolize all extinctions, although that wasn’t the cause in most of them. The five major extinctions come at the end of the Ordovician, Devonian, Permian, Triassic, and Cretaceous Periods. They are such important shapers of life that they are essential to a good timeline.
If all this correcting sounds like too much to do, remember that you are doing it for the children. They need current information and a foundation that they can use in their future studies. There is no point in giving them science “information” that they will never see outside a Montessori classroom.
In my last post, I took readers on an imaginary tour of nesting boxes for the plant kingdom. These materials are traditionally called Chinese boxes, but I prefer to use “nesting boxes.” Children explore the structure and major lineages of a kingdom of life with this material. Nesting boxes work well for showing the lineages of the animal kingdom provided the content reflects current knowledge.
Here’s an imaginary tour of nesting boxes for the animal kingdom as it is defined today. I believe firmly that we should be giving children terms that they will see in their further studies, not terms that are historical and that do not appear in modern textbooks.
To start our tour, picture a large red box labeled “Animal Kingdom.” We remove the lid, and inside there is a small box that is labeled “Phylum Porifera, the sponges.” This group was once called the Parazoa, but this term has fallen out of favor, and I recommend these animals be called the sponges. Once thought to be several separate lineages, they are now placed on one lineage, Porifera (“the pore-bearers”).
Along with the little Porifera box, there is a much larger box that takes up most of the animal kingdom box. It is labeled “Eumetazoa, the true animals.” We lift the lid, and inside there are two small boxes labeled “Phylum Ctenophora, the comb jellies” and “Phylum Cnidaria, the stingers.” A large box labeled “Bilateria” takes up most of the remaining space, and it holds the animals with bilateral symmetry.
Cnidarians include the sea anemones, corals, and jellyfish. The comb jellies include sea gooseberries and sea walnuts. These two phyla were previously placed in a single phylum. That phylum, Coelenterata, is obsolete and should not appear in current animal kingdom classification studies. Our small red boxes are labeled “Phylum Cnidaria, the stingers,” and “Phylum Ctenophora, the comb-bearers,” and “Coelenterata” is not here at all.
The big box labeled “Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry” contains two boxes, which are labeled Protostomes (“mouth first”) and Deuterostomes (“mouth second”). These names reflect a difference in the development of the fertilized egg in these two lineages. The deuterostome box takes up about 1/3 of the space. We look inside it, and we find two boxes, one labeled “Phylum Echinodermata, the spiny skins,” and the other “Phylum Chordata, the corded ones.” The echinoderm box has the sea urchins, sea stars, and sea cucumbers inside. The chordate box has its three subphyla inside, the lancelets, the tunicates, and the vertebrates. Note that chordates are not the same as vertebrates! I’ve seen them mistakenly equated in Montessori materials. (If you find the term “non-chordate” in your materials, it would be best to change it to “invertebrate.”)
The protostome box has two boxes inside, one labeled “Spiralia” or “Lophotrochozoa” and one labeled “Ecdysozoa.” The Spiralia box has the rotifers, the flatworms, the mollusks, and the annelids (segmented worms). This box also has the name Lophotrochozoa although some biologists use this cumbersome term for only a part of the Spiralia. The term Spiralia could change so check again in a few years to see the current story. The Spiralia are named for the pattern of cells in the early embryos of most species.
“Lophotrochozoa” is still used for the Spiralia lineage in many college textbooks, but this could to change by the time elementary children reach college age. I have adopted “Spiralia” because of biologists’ support for it, and it is easier to spell and say. My book, Kingdoms of Life Connected, still has “Lophotrochozoa” because when I reprinted it last year, the term “Spiralia” was not yet shown in Wikipedia (usually a good source for the latest phylogeny). I hope biologists have settled on the name by the time I print the book again.
The ecdysozoa are the molting animals. They shed their whole outer covering at once. This is the most successful animal lineage in terms of numbers of species and numbers of individuals. The Phylum Arthropoda, the jointed feet, and the Phylum Nematoda, the roundworms, are the two main phyla in this box. Tardigrades and velvet worms could also go here if space allows and if you want to get that level of detail.
If any of your animal kingdom materials include “protozoa,” please remove them and study them with the eukaryotic supergroups (protists). They do not belong in the animal kingdom. If your nesting boxes for animals have protozoa, the best time to change this was about 40 years ago. The second best time is now.
I’ve presented a basic look at the animal kingdom here. If you would like further information on the animal kingdom or the lineages I gave in this article, please see my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected. https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/kingdoms-of-life-connected-second-edition (printed) and https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/kingdoms-of-life-connected-ebook-1 (pdf).

If you want to evaluate an animal kingdom chart, look for the groupings I gave for the nesting boxes. The nematodes should be grouped with the arthropods. The echinoderms should be grouped with the chordates. This is because biologists group organisms according to their shared ancestors, not just how they look. The chart from InPrint for Children places related phyla next to each other. See https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/animal-kingdom-chart.

My photo card set for the animal kingdom - https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/zoology-photo-cards-set-1-major-phyla-of-the-animal-kingdom – gives you high quality images of representative animals across the kingdom. They could be used in or alongside a nesting box material.

Happy explorations of the animal kingdom,
Priscilla
PS. I am putting my reply here to two comments below. I'm sorry I don't have pictures of this imaginary material for you, Gail. I, too, am a visual learner. I think Cindy's idea of referring to the animal kingdom diagram from my Tree of Life chart might help. Yes, the lids on the boxes would be like a node on the evolutionary tree (phylogeny). The reason that there isn't a box for the Radiata is that they don't seem to share a common ancestor other than the one for all animals. If they did share a more recent ancestor, they might still be in Coelenterata. They have a similar organization, although the ctenophores are described as biradially symmetrical. They have a combination of radial and bilateral symmetry. The cnidarians are genuinely radially symmetrical. These two phyla came from separate experiments by early animal life. This is different than the the two phyla shown in the Ecdysozoa. They shared a common ancestor - at least there evidence for this in their genomes.
Thank you for sending your questions and comments. Please feel free to ask further questions.
Maria Montessori didn’t give guidance on updates. Why would she see the need to do this? The biology taught in her lifetime hardly changed.
If I asked you how you would divide the eukaryotes into groups, what would you say? Many people would say protists, fungi, animals, and plants. This is the idea presented in Five (or Six) Kingdoms classification. There is a more enlightening way to divide the eukaryotes, one that students currently see in introductory college courses.
The DNA revolution and the development of systematics rather than plain classification have given us a new view. Systematics includes the relationships between taxonomic categories instead of listing them with no information about their shared ancestors. It is a young science that has produced many changes and will likely produce many more.
This is not to say that we don’t have useable information right now. The largest categories of eukaryotes have been defined, and they are called the eukaryotic supergroups. There are four of them presently, and so the eukaryotes can be divided into four groups. Here’s an introduction to the archaeplastida, SAR, excavata, and unikonts aka Amorphea.
Archaeplastida is the lineage that acquired the first chloroplast. Its name means “ancient plastids.” A plastid is a type of organelle in a eukaryotic cell, and the category includes the chloroplast, whose name means “green body.” The archaeplastida lineage includes red algae and green algae, along with the embryophytes or land plants, which evolved from a green alga. This lineage is the only one that incorporated an ancient cyanobacterium into its cells. The origin of the chloroplasts in other lineages is a more complicated story.



The SAR lineage is named for the three main branches within it, stramenopiles, alveolates, and rhizarians. These lineages were defined independently and then researchers gathered enough evidence to conclude that they share a common ancestor. The stramenopiles (aka chromists or heterokonts) include brown algae, golden algae, diatoms, and water molds. Alveolates include dinoflagellates, apicomplexans (parasites such as malaria), and ciliates. The rhizarians include foraminiferans and radiolarians, single cell organisms that build amazing outer shells called tests.



And where did these branches of life get their chloroplasts? It seems that chloroplasts are NOT easy to acquire. Apparently, it is easier to take one from another cell than to acquire one by eating a cyanobacterium. An ancestor of the stramenopiles and alveolates probably ate a red alga and kept its chloroplasts. Euglenas, which we meet below, got their chloroplasts from a green alga.
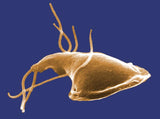
The third eukaryotic supergroup is the excavata, also called the excavates, but I see potential for confusion between the word as a noun vs. a verb. The lineage is named for a groove that looks like it has been excavated from the cells of some members. The excavata include the euglenas, which are free-living, and the trypanosomes, which are parasites. Other members of this group include the parasite Giardia and organisms that live in the guts of termites and help them break down cellulose. These have reduced mitochondria, so small that they were first described as lacking mitochondria.


I know you have been waiting for the last of the four supergroups, our own lineage, the unikonts (“single flagellum”) also known as the Amorphea (“having no form”). “Wait a minute,” you may be thinking, “we definitely have form.” The amoebas that belong to this lineage do not, however. The Amoebozoa lineage includes most of the slime molds or social amoebas as well as the single cell ones. Some of the latter build hard coverings (tests) for themselves. The other members of the unikonts are the fungus kingdom and the animal kingdom, which are sister kingdoms, having shared a common ancestor right before they branched off. There are other single cell organisms that are related to animals and fungi as well.



As you can see, the old protist kingdom had many different lineages of life shoe-horned into it, and the kingdoms that developed from its members were chopped off and boxed separately from it in the Five (or Six) Kingdoms scheme.
Why should you or your children learn about the supergroups of eukaryotes? It gives you a richer view of life and one that your children will see in their future studies. Will the names stay the same? Maybe, or maybe not, but these are the names in current college biology books, and it is worthwhile to learn about them and their members now.
Enjoy your explorations of the living world!
Priscilla
Like its counterpart, the animal kingdom chart, all Montessori elementary classrooms need a plant kingdom chart. A current version of this chart will have the same elements as a traditional one, but the groups will not have the same labels or arrangement as they have had in decades past. DNA studies and phylogenetic systematics have changed the look of the plant kingdom, and our charts need to reflect this. It is hard to find a solid consensus among botanists on the “right” names, but that is no excuse for giving names that we know are obsolete.
I’ve listed my recommendations for contents of a current plant kingdom chart below. The names that I think are most important are in boldface type. The other names may also be useful. Ask yourself, “Will elementary children be able to use this name to find information that they can read and understand?” If you do a search using the name, do you find information that you can use and understand? If not, consider dropping the more technical name and using the common name for the lineage, the one I emphasize below. The terms on charts for children should be useful for understanding the diversity of life AND for finding further information.
Plant Kingdom (land plants, embryophytes)
Bryophytes (nonvascular plants)
Liverworts (Phylum Marchantiophyta)
Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta)
Hornworts (Phylum Anthoceratophyta)
Vascular Plants or Tracheophytes
Lycophytes or club mosses and relatives (Phylum Lycophyta)
Euphyllophytes, the “true-leaf” plants
Fern clade or Monilophytes (Class Polypodiopsida)
Whisk ferns and relatives
Equisetums or horsetails
Ferns or leptosporangiate ferns or true ferns
Seed plants or Spermatophytes
Gymnosperms
Cycads (Phylum Cycadophyta)
Ginkgo (Phylum Ginkgophyta)
Gnetophytes (Phylum Gnetophyta)
Conifers (Phylum Pinophyta)
Angiosperms or flowering plants (Phylum Magnoliophyta)
Basal angiosperms
Magnoliids
Monocots
Eudicots
For a beginner’s chart, I start the plant kingdom with the land plants, the embryophytes. It is acceptable to add the green algae because they are closely related to embryophytes, but it is clearer if children learn about land plants first, and then add their relatives. Advanced students are ready for a chart of the Viridiplantae (green plants), which includes the green algae lineages and the land plants. It is important for children to understand that land plants and green algae share a common ancestor.
Don’t feel bad about leaving off phylum/division names. While the animal kingdom phyla have been rearranged by DNA studies, they have kept their names. Plant kingdom phyla or divisions, whichever you wish to call them, aren’t as useful anymore. In fact, I have a widely-used, advanced textbook for plant systematics that uses no phylum/division names at all. Instead, it simply uses names with no ranks for the major lineages, such as lycophytes, euphyllophytes, seed plants, and angiosperms. It still uses orders, families, genera, and species, the Linnaean ranks that botanists continue to use for plants.
There has been a big change that centers on the ferns. An older scheme had four phyla, Psilophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Pterophyta or Pteridophyta. These groups, often called “ferns and fern allies,” were considered more or less equal, but now we know that the lycophytes are a separate lineage from the other three. The fern clade, now considered by some to be a phylum, has three groups once considered separate phyla – the whisk ferns, horsetails, and the true ferns.
I see no reason to put notably out-of-date information on a plant kingdom chart. I especially encourage you to remove any images that are no longer considered plants. If you still have a mushroom on your plant kingdom chart, children are going to associate fungi with plants, even if you tell them that we know now that fungi are closely related to the animal kingdom and not at all close to plants. The visual impression that a chart gives to children is powerful, and it is important to get it as close to current as we can.
Change seems to come slowly in the general knowledge of plant systematics. I did an Internet search for plant kingdom charts and classification, and I found an amazing range of information from very old to current. Some websites even use the terms “cryptogams” and “phanerogams,” which came into use about 1860. Botanists haven’t used them in academic publications for at least 40 years. It is not that they are “wrong,” but they describe a superficial view that botanists had over a century ago. Our knowledge has grown, and there are better ways of expressing the differences among plant groups.
The flowering plants are currently divided into several lineages. I listed the main ones above, basal angiosperms, magnoliids, monocots, and eudicots. Botanists no longer use only the monocot and dicot subgroups, although these are still common in field guides and older publications. The flowering plants make up about 90% of the plant kingdom, and their orders have been defined in the last two or three decades using DNA studies. They deserve their own chart of orders and families.
My plant kingdom chart from my Tree of Life shows the lineages and their relationships. The plant kingdom chart from InPrint for Children gives children more practice with the categories.

Here are some quick ways to check the information on a plant kingdom chart for your classroom. If the chart shows a row of evenly spaced boxes, it isn’t giving children all the information they need. Bryophytes need to be grouped together and somehow spaced apart from the tracheophytes. Lycophytes should be separated from other spore-producing plants. If the club mosses, whisk ferns, true ferns, and horsetails are all grouped together and perhaps called “fern allies” or “pteridophytes,” that’s obsolete. There should be something to show that the club mosses are a different lineage from the three branches of the fern clade, and if possible, that ferns are more closely related to seed plants. If the term “dicots” or “dicotyledons” appears instead of “eudicots,” then that needs to change. Eudicots (“true dicots”) are the old dicots minus the magnoliids and the basal lineages such as water lilies.
The same criteria for illustrations on a kingdom chart apply to animals and plants. Can you see the important structural features that enable children to recognize the lineage? For example, can you see a fern’s fiddleheads or its sori? Can you see the sporophytes of the bryophyte lineages? Sporophytes need to be visible and described in the text. The reproductive structures and foliage of the gymnosperms help children tell the difference between those lineages. Flower illustrations should clearly show stamens and pistils. Consider showing a fruit as well because fruits are unique to the flowering plants.
In the text for the chart, give children a range of examples whenever this is possible. Children, like much of our society, are less likely to be familiar with plants than they are with animals. They may be surprised to learn that grasses, maples, and oak trees are flowering plants.
Enjoy opening children’s eyes to the diversity of plants! For more information about the plant kingdom and its members, see my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected.
A chart of the animal kingdom is standard equipment for any Montessori elementary classroom. The chart could be purchased or made by the guiding adult. Either can be appropriate and useful to children. Conversely, either can have significant mistakes and misconceptions. Here are guidelines for choosing or making an animal kingdom chart.
First of all, the animal kingdom chart presents the major phyla. “What are those phyla?” you may ask. There are about 35 phyla of animals, and that is far too many to present to elementary children. Some have few members, and children are not likely to ever experience their members. The Wikipedia article on animals has a table that gives the number of species in the 11 largest phyla. Here is my list of phyla that show important structural features or notable evolutionary features. I consider the following “must haves” for the animal kingdom chart for beginning elementary.
Phylum Porifera, the sponges
Phylum Cnidaria, the anemones, jellyfish, corals, and hydras
Phylum Platyhelminthes, the flatworms
Phylum Annelida, the segmented worms – earthworms, leeches, and polychaete worms
Phylum Mollusca, the mollusks – snails, clams, octopuses, etc.
Phylum Nematoda, the nematodes or roundworms
Phylum Arthropoda, the arthropods – insects, crustaceans, spiders, and many others
Phylum Echinodermata, the echinoderms – starfish, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, etc.
Phylum Chordata, the chordates – lancelets, tunicates, and vertebrates (NOTE: Chordata is not equal to Vertebrata. The latter is a subphylum of Chordata.)
These belong on all animal kingdom charts to illustrate the range of creatures in this kingdom. There are other phyla of interest that can be added for a more advanced chart or one that spans elementary and secondary levels.
Phylum Ctenophora, the comb jellies – This phylum is significant because it is likely to be the second branch of the kingdom after the sponges. Ctenophores occur worldwide in marine waters. They were formerly grouped with the cnidarians in the obsolete phylum Coelenterata.
Phylum Rotifera, the rotifers – If children look at pond water under the microscope, it is likely that they will see these tiny animals. On a chart, rotifers would go near flatworms and segmented worms.
Phylum Ectoprocta or Bryozoa, the bryozoans or moss animals – Children are unlikely to observe these animals because they are about 0.5 mm across, but they may find bryozoan colonies at the beach. Use a guide to seashore life to identify them. Almost all bryozoans live in colonies, which can look like crusts on other organisms or rocks. Some form larger colonies that are commonly known as brown hairy tongues.
Phylum Brachiopoda, the brachiopods – These were much more common in the fossil record than they are now. The two halves of their shells enclose their top and bottom halves, whereas the two halves of a clam shell enclose the left and right sides of the mollusk’s body. This makes brachiopods a bit challenging for the beginner. I would hold this phylum for later introduction, perhaps along with studies of the Paleozoic Era.
Phylum Hemichordata – This small phylum of marine creatures includes acorn worms and pleurobranchs, which are tiny colonial animals. The extinct graptolites are placed in this phylum. Despite its name, this phylum is more closely related to echinoderms than to chordates. It is too confusing for beginners. Let children get a firm grasp of chordates before you introduce this phylum.
Other minor phyla – There is plenty for beginners to learn without adding minor phyla, however it is good to be prepared in case your children encounter an animal of a minor phylum. Many of these will be marine animals, and so a guide to marine life can be useful to place these finds into a phylum. Possibilities include ribbons worms, horsehair worms, velvet worms, and tardigrades.
Keep in mind why we are introducing children to various animal phyla. In this kingdom, each phylum has a different body plan. Children learn about the unique characteristics of each lineage. To this end, the illustrations on the chart should show at least one example that illustrates the identifying traits. Close up photos of a portion of the animal’s body or photos with a messy background or many animals together are not helpful for seeing the body plan of the organism.
Of course, the description of the phylum needs to include its scientific name. Don’t stop there, however. Children may not be able to find further information that they can read and understand unless they have common names as well. They likely know many of the common names, and it boosts learning to start with something known and move to new information.
The phylum description needs to state simply and straightforwardly the main features of that lineage. For example, segmented worms should be described as having repeated segments in their bodies. If you have a good illustration, it is easier to describe important visible features.
Finally, how do you arrange the phyla on the animal kingdom chart? HINT: It isn’t in an evenly-spaced straight line. Some phyla are more closely related than others. The animal kingdom chart that high school or college students will see is a phylogeny, a branching diagram. If you do not wish to start with a phylogeny, you can still group related phyla together. The echinoderms and the chordates are sister phyla. So are the nematodes and the arthropods. The mollusks and annelids are another closely related pair. The animal kingdom chart from InPrint for Children is a good example of grouping phyla.
For any studies of classification beneath the level of phyla, it is best to use a phylogeny. For an example, see my material, “From the Chordates to Mammals: Exploring the Tree of Life.” https://big-picture-science.myshopify.com/collections/biology/products/from-chordates-to-mammals-exploring-the-tree-of-life

Happy animal explorations! For more information about the animal phyla and the phylogeny of the animal kingdom, see my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected. 
For many years, I have promoted the idea of structuring botany around the flowering plant families. It’s a practical way of addressing the diversity of the angiosperms, and it is knowledge that works in many places and at many levels. For instance, organic gardeners need to know the families of vegetables so that they can do the proper crop rotation and fertilizing. Plant identification is much easier if one can determine the family. Flowers in the same family share certain features, so it is quite possible to recognize the family even if you have never seen that species before.
 To help you with your botany studies, I’ve just revised and expanded my PowerPoint slides on flowering plant families. This file is a pdf that can be printed to make letter-sized posters of 20 flowering plant families. The slides include text that describes the features of the flowers, and they show photos of family members. To round out this material, I’ve added a representative photo of 48 other families or subfamilies from all branches of the angiosperms.
To help you with your botany studies, I’ve just revised and expanded my PowerPoint slides on flowering plant families. This file is a pdf that can be printed to make letter-sized posters of 20 flowering plant families. The slides include text that describes the features of the flowers, and they show photos of family members. To round out this material, I’ve added a representative photo of 48 other families or subfamilies from all branches of the angiosperms.
 Perhaps you would like to do a Tree of Life diagram for the flowering plants. There is a good one in the book, Botanicum by Katie Scott and Kathy Willis. It is part of the Welcome to the Museum series from Big Picture Press (no relation to Big Picture Science), and it was published in 2016. The branches are correct on the diagram (pages 2 and 3), but they have just one example for each branch, and the orders are not stated. The example represents a whole order, which leaves out a lot. For example, the rose order, Rosales, is represented by a mulberry leaf. Mulberries and figs belong to family Moraceae, which is in the rose order, along with rose, elm, buckthorn, hemp, and nettle families. On the other hand, the diagram fits on two pages. It have to be much larger to be more comprehensive. All-in-all, the book is delightful and will provide lots of fun browsing. You will have to tell children that the page on fungi is a holdover from earlier definitions of botany.
Perhaps you would like to do a Tree of Life diagram for the flowering plants. There is a good one in the book, Botanicum by Katie Scott and Kathy Willis. It is part of the Welcome to the Museum series from Big Picture Press (no relation to Big Picture Science), and it was published in 2016. The branches are correct on the diagram (pages 2 and 3), but they have just one example for each branch, and the orders are not stated. The example represents a whole order, which leaves out a lot. For example, the rose order, Rosales, is represented by a mulberry leaf. Mulberries and figs belong to family Moraceae, which is in the rose order, along with rose, elm, buckthorn, hemp, and nettle families. On the other hand, the diagram fits on two pages. It have to be much larger to be more comprehensive. All-in-all, the book is delightful and will provide lots of fun browsing. You will have to tell children that the page on fungi is a holdover from earlier definitions of botany.
The photos of families from my newly revised Flowering Plant Families Slides can be used to create a Tree of Life that has many orders. It gives a broader look at the families than its predecessor, and it is still centered on the families of North America. There are over 400 families of angiosperms worldwide. You don’t need to worry about being anywhere near comprehensive when you introduce children to flower families. Select the main ones for which you have examples from your school landscape, in areas near the school, or as cut flowers. If you or your children want to see the full list, go to the Wikipedia article on APG IV system (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV).
 I’m not the only one that advocates structuring botany studies around flowering plant families. Thomas Elpel has written a highly successful book called Botany in a Day: The Pattern Method of Plant Identification. It is further described as “An Herbal Field Guide to Plant Families of North America.” This book is in its sixth edition. It has color drawings as well as black and white ones, and these could be useful in classrooms. I have not recommended placing this book in the elementary classroom, however, because it includes many food and medicinal uses for wild plants. I do not want to encourage children to eat wild plants or use them as medicine.
I’m not the only one that advocates structuring botany studies around flowering plant families. Thomas Elpel has written a highly successful book called Botany in a Day: The Pattern Method of Plant Identification. It is further described as “An Herbal Field Guide to Plant Families of North America.” This book is in its sixth edition. It has color drawings as well as black and white ones, and these could be useful in classrooms. I have not recommended placing this book in the elementary classroom, however, because it includes many food and medicinal uses for wild plants. I do not want to encourage children to eat wild plants or use them as medicine.
 Botany in a Day is available from Mountain Press Publishing in Missoula, Montana, which also carries Elpel’s flower family book for children, Shanleya’s Quest. This book is a great one for elementary classrooms, and I strongly recommend it.
Botany in a Day is available from Mountain Press Publishing in Missoula, Montana, which also carries Elpel’s flower family book for children, Shanleya’s Quest. This book is a great one for elementary classrooms, and I strongly recommend it.
Enjoy exploring and identifying the flowers!
 The second edition of my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected: A Teacher’s Guide to the Tree of Life, is available now. I wrote the first edition in 2008, and it was already time for an update this year. New information keeps coming in all fields of science. This leads to gradually evolving ideas, but change has been exceptionally rapid in the field of systematics, the study of the diversity of life.
The second edition of my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected: A Teacher’s Guide to the Tree of Life, is available now. I wrote the first edition in 2008, and it was already time for an update this year. New information keeps coming in all fields of science. This leads to gradually evolving ideas, but change has been exceptionally rapid in the field of systematics, the study of the diversity of life.
The flood of DNA information continues, and we must bear that in mind in our presentations. It would be better to state that the story you tell is based on the evidence scientists have gathered for now. In the future, there could be adjustments. This doesn’t mean that all the information about the Tree of Life will change. Instead there will be small alterations. The potential for change certainly doesn’t excuse the presentation of obsolete classifications as anything other than history.
One of the hardest tasks for my book revision was finding up-to-date children’s books about the diversity of life. I had to leave many older, but valuable, books on the resource lists. At least it is easier to find out-of-print books now than it was a decade ago. I also found that publishers have reprinted some valuable older books. They include Peter Loewer’s Pond Water Zoo: An Introduction to Microscopic Life. Jean Jenkins illustrated this book in black and white, and it has attractive, clear drawings of many protists, bacteria, and microscopic animals, along with text that upper elementary children can read. You will have to warn your children that the classification scheme presented, the Five Kingdoms, is obsolete, but the information about the groups of organisms is still quite good.
A forty-year-old book by Alvin and Virginia Silverstein, Metamorphosis: Nature’s Magical Transformations, has been reprinted by Dover Books. It has a chapter on sea squirts that shows the tadpole-like larval stage and tells about the life cycle of these chordates. I haven’t found another children’s book that tells this story. The black and white illustrations show how old the book is, but there didn’t seem to be a good alternative.
I know the pain of having to purchase a new edition of a reference book. My favorite biology textbook cost nearly $200, and I see the new edition, just published this month, is priced at $244. Yikes, that’s hard on the budget. If you own the first edition of Kingdoms of Life Connected, you will be able to purchase the ebook version – the pdf file – of the book at a reduced price. Please email info (at) bigpicturescience (dot) biz for information about how to do this.
























 To help you with your botany studies, I’ve just revised and expanded my PowerPoint slides on flowering plant families. This file is a pdf that can be printed to make letter-sized posters of 20 flowering plant families. The slides include text that describes the features of the flowers, and they show photos of family members. To round out this material, I’ve added a representative photo of 48 other families or subfamilies from all branches of the angiosperms.
To help you with your botany studies, I’ve just revised and expanded my PowerPoint slides on flowering plant families. This file is a pdf that can be printed to make letter-sized posters of 20 flowering plant families. The slides include text that describes the features of the flowers, and they show photos of family members. To round out this material, I’ve added a representative photo of 48 other families or subfamilies from all branches of the angiosperms.  Perhaps you would like to do a Tree of Life diagram for the flowering plants. There is a good one in the book, Botanicum by Katie Scott and Kathy Willis. It is part of the Welcome to the Museum series from Big Picture Press (no relation to Big Picture Science), and it was published in 2016. The branches are correct on the diagram (pages 2 and 3), but they have just one example for each branch, and the orders are not stated. The example represents a whole order, which leaves out a lot. For example, the rose order, Rosales, is represented by a mulberry leaf. Mulberries and figs belong to family Moraceae, which is in the rose order, along with rose, elm, buckthorn, hemp, and nettle families. On the other hand, the diagram fits on two pages. It have to be much larger to be more comprehensive. All-in-all, the book is delightful and will provide lots of fun browsing. You will have to tell children that the page on fungi is a holdover from earlier definitions of botany.
Perhaps you would like to do a Tree of Life diagram for the flowering plants. There is a good one in the book, Botanicum by Katie Scott and Kathy Willis. It is part of the Welcome to the Museum series from Big Picture Press (no relation to Big Picture Science), and it was published in 2016. The branches are correct on the diagram (pages 2 and 3), but they have just one example for each branch, and the orders are not stated. The example represents a whole order, which leaves out a lot. For example, the rose order, Rosales, is represented by a mulberry leaf. Mulberries and figs belong to family Moraceae, which is in the rose order, along with rose, elm, buckthorn, hemp, and nettle families. On the other hand, the diagram fits on two pages. It have to be much larger to be more comprehensive. All-in-all, the book is delightful and will provide lots of fun browsing. You will have to tell children that the page on fungi is a holdover from earlier definitions of botany. I’m not the only one that advocates structuring botany studies around flowering plant families. Thomas Elpel has written a highly successful book called Botany in a Day: The Pattern Method of Plant Identification. It is further described as “An Herbal Field Guide to Plant Families of North America.” This book is in its sixth edition. It has color drawings as well as black and white ones, and these could be useful in classrooms. I have not recommended placing this book in the elementary classroom, however, because it includes many food and medicinal uses for wild plants. I do not want to encourage children to eat wild plants or use them as medicine.
I’m not the only one that advocates structuring botany studies around flowering plant families. Thomas Elpel has written a highly successful book called Botany in a Day: The Pattern Method of Plant Identification. It is further described as “An Herbal Field Guide to Plant Families of North America.” This book is in its sixth edition. It has color drawings as well as black and white ones, and these could be useful in classrooms. I have not recommended placing this book in the elementary classroom, however, because it includes many food and medicinal uses for wild plants. I do not want to encourage children to eat wild plants or use them as medicine. Botany in a Day is available from Mountain Press Publishing in Missoula, Montana, which also carries Elpel’s flower family book for children, Shanleya’s Quest. This book is a great one for elementary classrooms, and I strongly recommend it.
Botany in a Day is available from Mountain Press Publishing in Missoula, Montana, which also carries Elpel’s flower family book for children, Shanleya’s Quest. This book is a great one for elementary classrooms, and I strongly recommend it. The second edition of my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected: A Teacher’s Guide to the Tree of Life, is available now. I wrote the first edition in 2008, and it was already time for an update this year. New information keeps coming in all fields of science. This leads to gradually evolving ideas, but change has been exceptionally rapid in the field of systematics, the study of the diversity of life.
The second edition of my book, Kingdoms of Life Connected: A Teacher’s Guide to the Tree of Life, is available now. I wrote the first edition in 2008, and it was already time for an update this year. New information keeps coming in all fields of science. This leads to gradually evolving ideas, but change has been exceptionally rapid in the field of systematics, the study of the diversity of life.